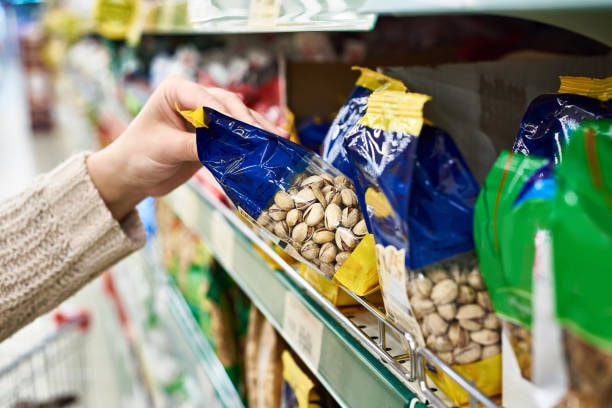
Choosing the right raw materials for your plastic packaging can mean the difference between a product that stays fresh and one that quickly loses its appeal.
In the competitive food industry, where freshness, safety, and sustainability matter, selecting the best food-safe, flexible materials is critical. Food manufacturing companies utilize various forms of plastic packaging for different food products, highlighting the flexibility and economic advantages of plastics, such as PET, for packaging liquids and solid foods.
Whether you’re packaging snacks, frozen meals, or ready-to-eat products, the right food packaging ensures product protection, extends shelf life, and even supports eco-friendly goals by incorporating recycled or recyclable materials.
In this post, we’ll break down how to choose the perfect flexible plastic packaging material that meets your needs while keeping your products fresh, safe, and market-ready.
Selecting the correct type of food packaging film is essential for keeping food products safe, fresh, and ready for customers. Various materials are designed to protect food during storage and transportation, ensuring food preservation throughout the supply chain.
The correct packaging can extend the shelf life of food products by blocking out moisture, air, and harmful bacteria. It also helps prevent contamination and keeps food tasting its best.
On the flip side, using the wrong packaging can cause food to spoil faster, become contaminated, or even get damaged before reaching the customer. This can result in wasted products, lost revenue, and unhappy customers.
Food manufacturers use different packaging films based on their physical and chemical properties to ensure superior protection for food products. Here are three commonly used types:
- Plastics: Plastic resins like polyethylene, polypropylene, polyester, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to moisture. They are ideal for sealing and protecting food, offering superior protection against air, bacteria, and spoilage. Plastic bottles are significant in food packaging due to their lightweight, impact resistance, and versatility for various liquids. PET bottles have effectively replaced traditional glass bottles due to lower risks of breakage and shipping complications.
- Metals: Aluminum, steel, and tin provide strong physical properties like durability and resistance to corrosion. Their ability to block light, air, and moisture makes them perfect for preserving canned and packaged foods for extended periods.
- Cellulose: Cellulose-based materials such as cellophane and cellulose acetate are biodegradable and sustainable. They are eco-friendly alternatives while maintaining necessary safety and protection standards.
Food packaging films must balance safety, durability, and sustainability while keeping storage costs manageable. Here’s why these features matter:
- Safety: Materials should be food-safe, suitable for direct contact materials, and prevent contamination from chemicals, bacteria, and moisture. For shelf-stable products, safe packaging keeps food fresh and extends its usability.
- Durability: Packaging should endure transportation, storage, and handling without tearing, leaking, or breaking. While cheaper materials may reduce upfront expenses, they can cause product damage if not sturdy enough, increasing long-term costs.
- Sustainability: With rising environmental concerns, many brands are switching to recycled materials or biodegradable options. Sustainable packaging helps reduce environmental impact while meeting regulatory and consumer expectations
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets requirements for sustainable packaging mandates in various regions.
Balancing these factors ensures food stays protected, shelf-stable, and eco-friendly while keeping operational expenses in check.
Aropack Packaging Ltd. is at the forefront of sustainable flexible packaging, offering monomaterial solutions that help brands reduce their environmental impact without compromising on quality.
Plastics are essential in food packaging due to their durability, flexibility, and barrier properties. The versatility and practicality of plastic films make them ideal for a variety of food items, from liquids to solid snacks. Here’s a closer look at common types:
-
Polyethylene: Available as low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), this plastic is flexible, lightweight, and moisture-resistant, making it ideal for food storage bags and wraps.
-
Polypropylene: Known for its durability and moisture resistance, polypropylene is commonly used for containers and packaging films.
-
Polyester: Also called polyethylene terephthalate (PET), this strong and lightweight plastic provides excellent barrier protection against air and moisture.
-
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC is flexible and has strong sealing properties, making it useful for packaging fresh produce and meats.
As sustainability becomes a priority, biodegradable and compostable materials like PLA and PHA are increasingly used in food packaging:
-
Polylactic Acid (PLA): Made from renewable resources like corn starch, PLA is a biodegradable plastic commonly used for food containers, cups, and wraps. It breaks down naturally under composting conditions, reducing plastic packaging waste.
-
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): Produced by natural fermentation of plant-based materials, PHA is fully biodegradable and compostable. It offers durability similar to traditional plastics while being eco-friendly, making it ideal for food packaging that supports sustainability goals.
Cellulose-based materials are popular in food packaging because they are biodegradable and eco-friendly. Here’s a closer look at two common types:
-
Cellophane: Made from natural cellulose derived from plants, cellophane is biodegradable and provides a clear, moisture-resistant barrier. It is commonly used for wrapping baked goods, candies, and other food products.
-
Cellulose Acetate: This plant-based material is known for its strength and transparency. It is often used in food trays, films, and wrapping materials. Its biodegradable nature makes it a sustainable choice for companies aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
When selecting food packaging materials, ensuring product compatibility is crucial to maintain safety and freshness. Packaging must be safe for direct food contact and prevent contamination from harmful chemicals.
Materials like low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) are popular packaging material since they are moisture-resistant, and durable.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is another popular option due to its excellent barrier properties against air and moisture.
The material should also be chemically stable, preventing unwanted reactions between the packaging and the food it contains. This ensures products remain fresh, safe, and ready for consumption.
Food packaging materials play a critical role in extending a product’s shelf life by protecting it from spoilage. To keep food fresh, materials must have strong barrier properties that block moisture, oxygen, and light—which can degrade products, especially wet foods and acidic foods. For example, PET films are common materials due to its excellent barrier against air and moisture.
Aluminum foil and multi-layer films are also popular for their durability and ability to block light, making them ideal for packaging acidic foods that require extra protection from moisture, air, and external contaminants.
Food packaging materials should not only protect products but also support clear brand image and eye-catching designs. High-quality printing helps display product information, logos, and branding elements effectively, making products stand out on store shelves.
Materials like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are commonly used because they allow for sharp, vibrant printing. Multi-layer films also offer smooth surfaces ideal for custom designs and labeling.
Clear, well-printed packaging builds brand recognition and attracts customers while ensuring essential details like product names, ingredients, and expiration dates remain readable and professional-looking throughout the product’s shelf life.
The best food packaging materials are those that balance product protection with sustainability. Flexible packaging made from recyclable or biodegradable materials helps reduce plastic waste and lower the carbon footprint of product packaging.
Recyclable packaging like mono-PE films and biodegradable options such as polylactic acid (PLA) or cellulose-based films are popular eco-friendly choices. These materials decompose naturally or can be reused, minimizing environmental harm.
Choosing food packaging materials involves balancing cost, customer expectations, and sustainability goals. Businesses need packaging that protects products while staying within budget. However, customers increasingly expect eco-friendly packaging that aligns with environmental values.
Sustainable options like recycled plastics, biodegradable films, and compostable paper may cost more but appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
The flexible packaging industry is evolving with new materials and technologies that balance cost-efficiency and sustainability.
Emerging technologies include water-soluble packaging, bio-based plastics like polylactic acid (PLA), and recycled content integration.
Food packaging films must meet strict safety and quality standards set by national and international regulations. These rules ensure that materials are safe for food contact and prevent contamination.
Key regulations include U.S. FDA guidelines, EU food safety directives, and industry-specific standards. Packaging must also meet labeling, sustainability, and recyclability requirements where applicable.
The food packaging industry constantly evolves due to changing regulations and technological advancements. Food manufacturers must stay informed about new packaging standards to ensure compliance and maintain product safety.
When selecting food packaging, it’s crucial to consider the entire supply chain—from manufacturing to the consumer’s hands. Each stage presents unique challenges, such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to light.
Packaging materials must be robust enough to withstand these conditions without compromising the product’s integrity. By understanding the journey your product takes, you can choose packaging materials that offer optimal protection at every stage.
The type of equipment used in the manufacturing process significantly influences the choice of packaging materials.
Flexible packaging machinery, such as form-fill-seal or pouch-making machines, requires materials that can perform well under specific conditions. For example, materials like polyethylene (PE) and polyester (PET) are often preferred for their compatibility with high-speed packaging lines and their ability to form strong seals.
To make informed decisions about packaging materials, manufacturers need to rely on quantitative measurements. This involves assessing the material’s barrier properties, such as its ability to block moisture, oxygen, and light, which are critical for extending shelf life.
Additionally, evaluating the material’s strength and durability ensures it can withstand the rigors of transportation and handling.
Cost per unit is another vital factor; materials like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are often chosen for their cost-effectiveness without compromising quality. By balancing these quantitative assessments, manufacturers can select packaging materials that meet both performance requirements and budget constraints.
When choosing materials for flexible packaging, it’s important to balance safety, durability, and sustainability. Packaging must be food-safe to prevent contamination, durable enough to survive shipping and handling, and eco-friendly.
Materials should also match the product’s needs. For example, flexible pouches work well for pet food, frozen foods or snacks while tin cans are better for preserving long-shelf-life items.
We provide tailored solutions to help you make the best choice for your business. Whether you need the high-performance features of laminated films or the sustainability benefits of monomaterial options, our team is here to guide you every step of the way.
Give us a call on 01233 281460 or send us an email at info@aropack.co.uk for a consultation. Let us help you find the perfect balance between sustainability and functionality.